Halassa Lab
Project 2
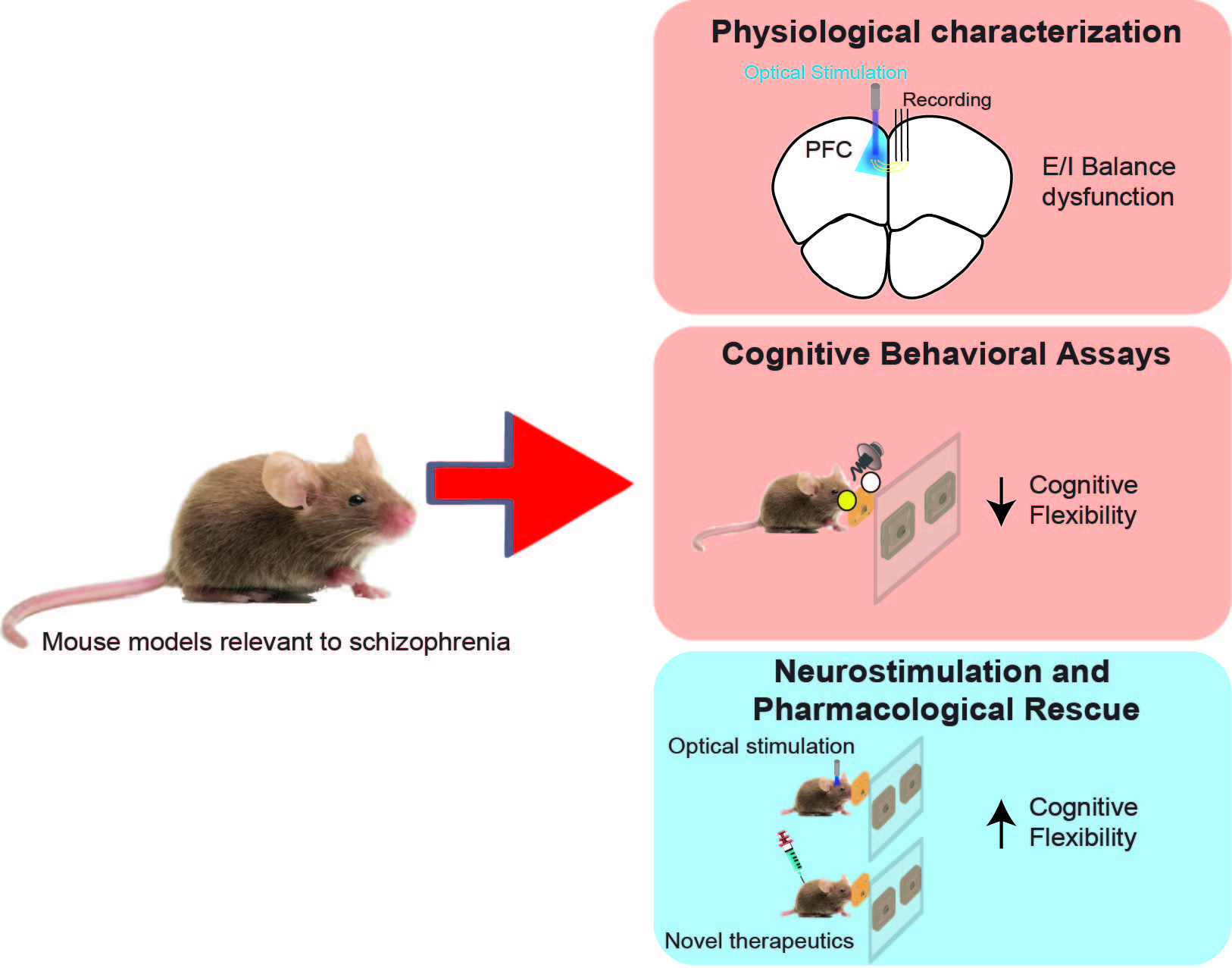
The relationship between schizophrenia-relevant prefrontal E/I balance perturbations and specific cognitive deficits:
Schizophrenia is a disorder affecting millions worldwide, with almost all cases exhibiting some cognitive dysfunction. Improving cognitive function in these individuals could restore up to 1% of the global workforce. Although it is recognized that schizophrenia is associated with prefrontal dysfunction, E/I imbalance and cognitive deficits, how these three domains are linked together through a unifying framework is unclear. To at least partly address this issue, we are making prefrontal network E/I measurements in multiple mouse models relevant to schizophrenia, including the 22q11 deletion model, and attempting to connect individual metrics to changes in PFC-dependent task behavioral parameters. The brain-behavior correlates identified in this work appear to respond to targeted neurostimulation and novel pharmacological treatment. The metrics characterized in these mouse-models relevant to schizophrenia provide insight into the mechanisms contributing to cognitive deficits in schizophrenia, as well as new avenues for treatment.
Address
Tufts University School of Medicine
Neuroscience Department
136 Harrison Ave., Boston, MA 02111
Accessibility
Tufts is committed to making physical and online resources available to everyone.
You Are Welcome Here
Halassa Lab is committed to creating a diverse environment. All qualified applicants will receive consideration for employment without regard to race, color, religion, gender, gender identity or expression, sexual orientation, national origin, genetics, disability, age, or veteran status.
